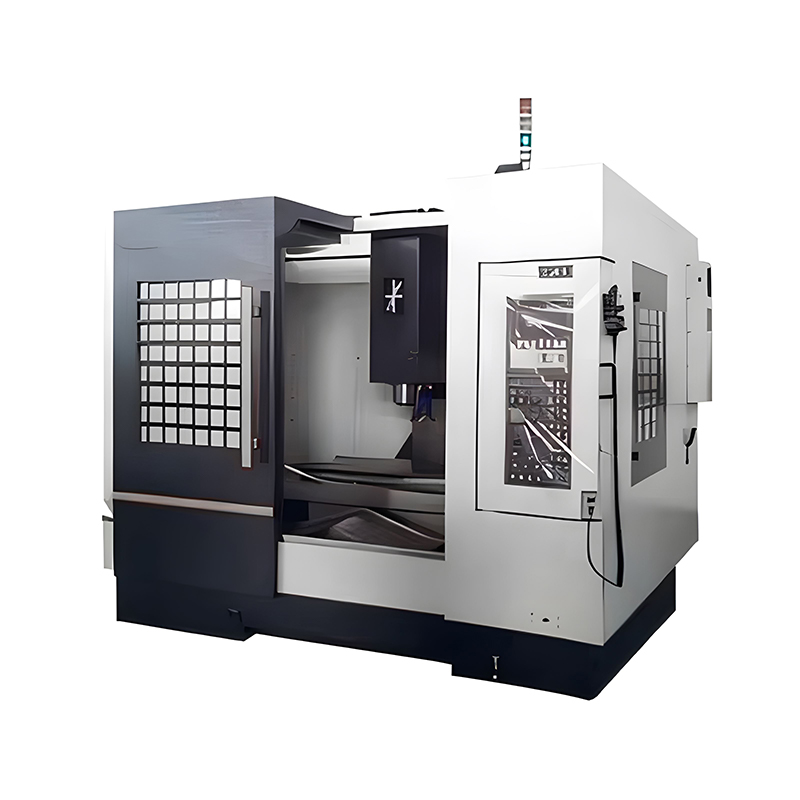
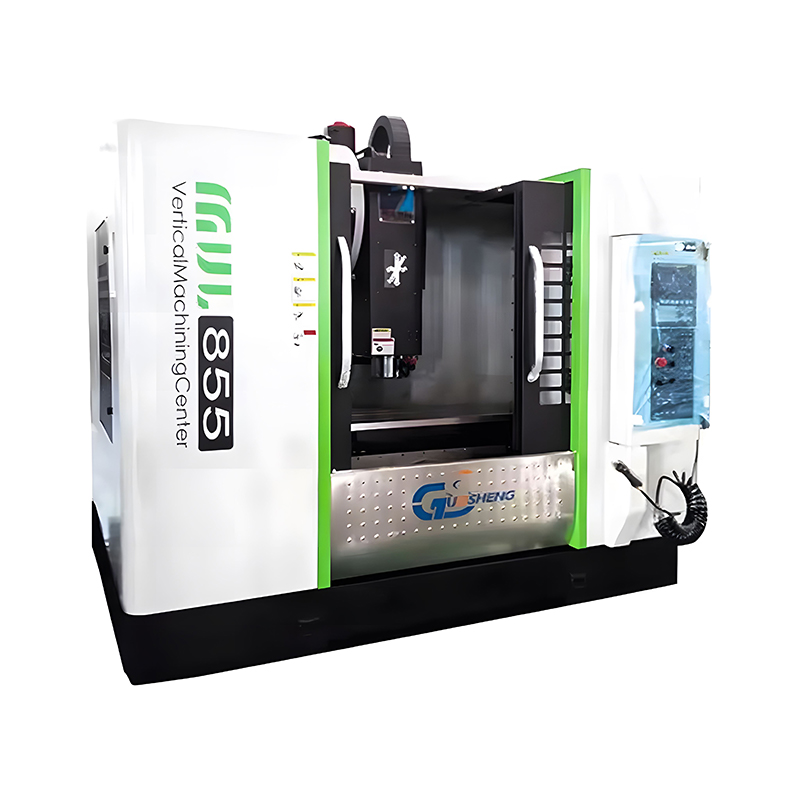
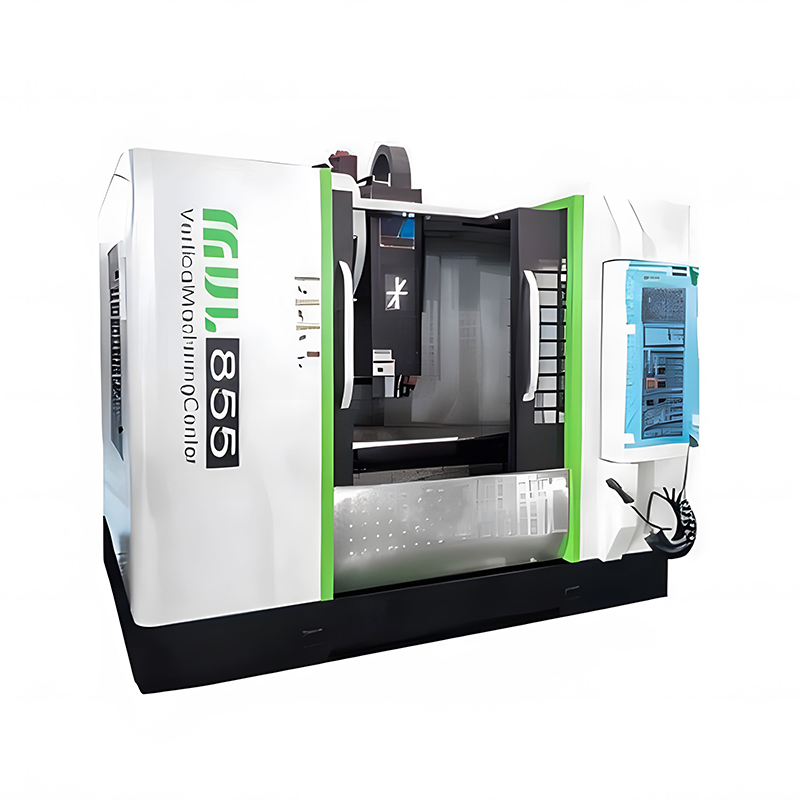
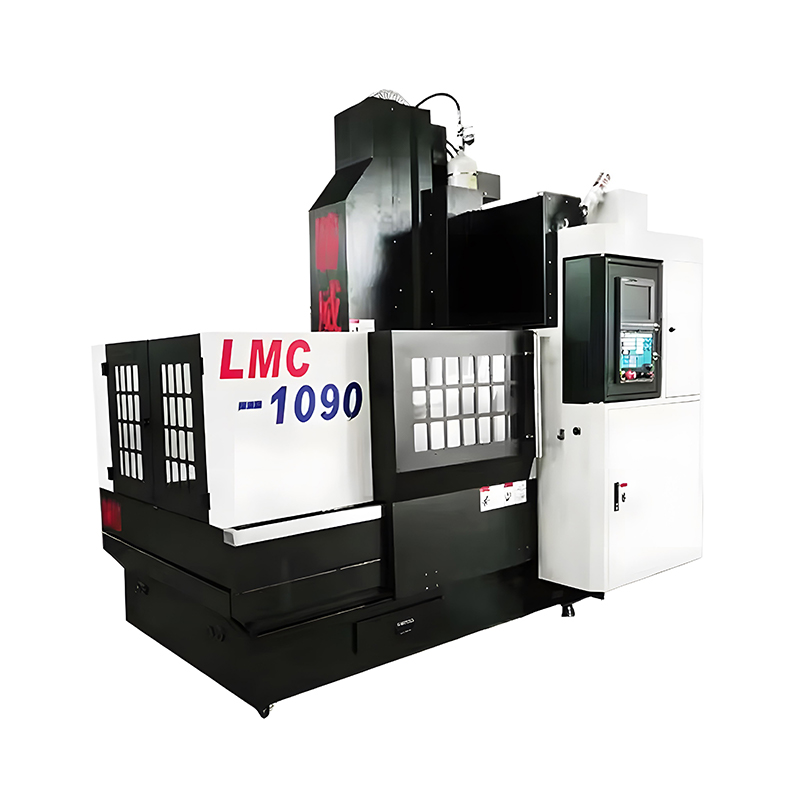
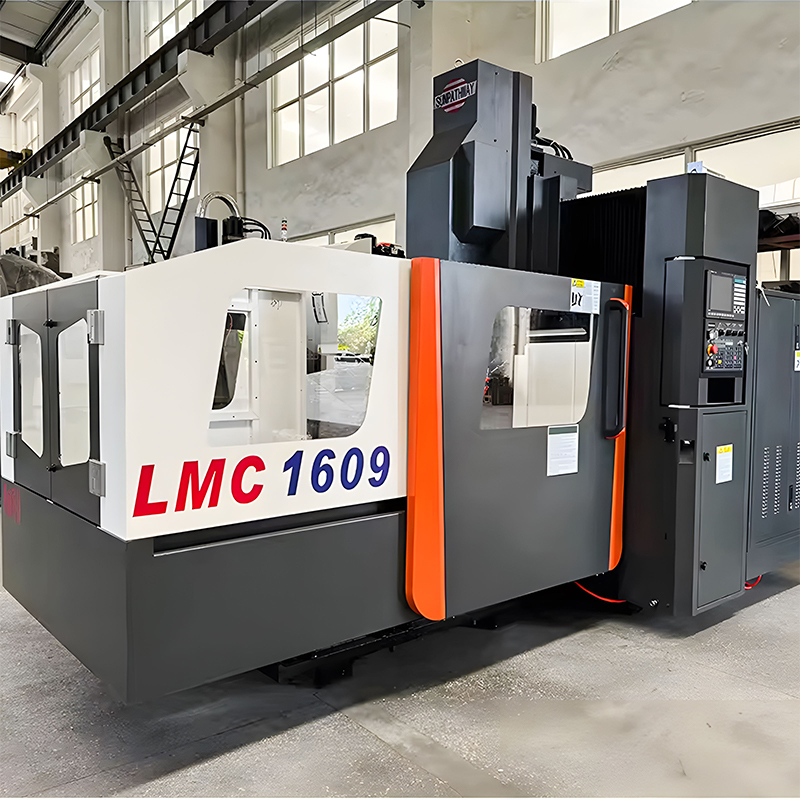
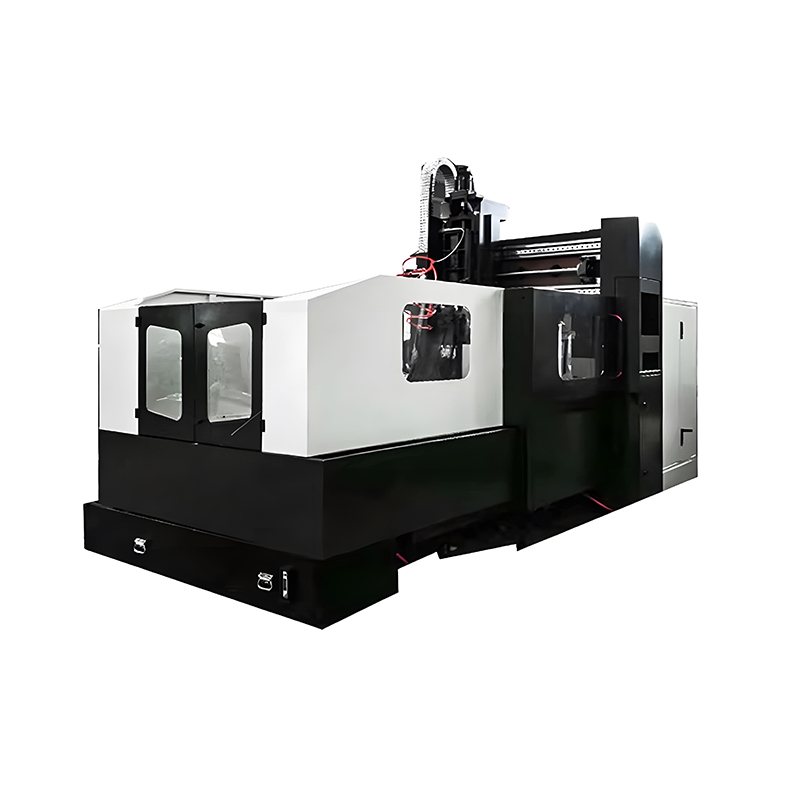
Top Tier Manufacturers of Vertical Machining Centers When searching for the industry leaders in vertical machining centers, several names consistently dominate the market based on reliability, precision, and technological innovat...
READ MOREWe provide quality products and services to customers from all over the world.
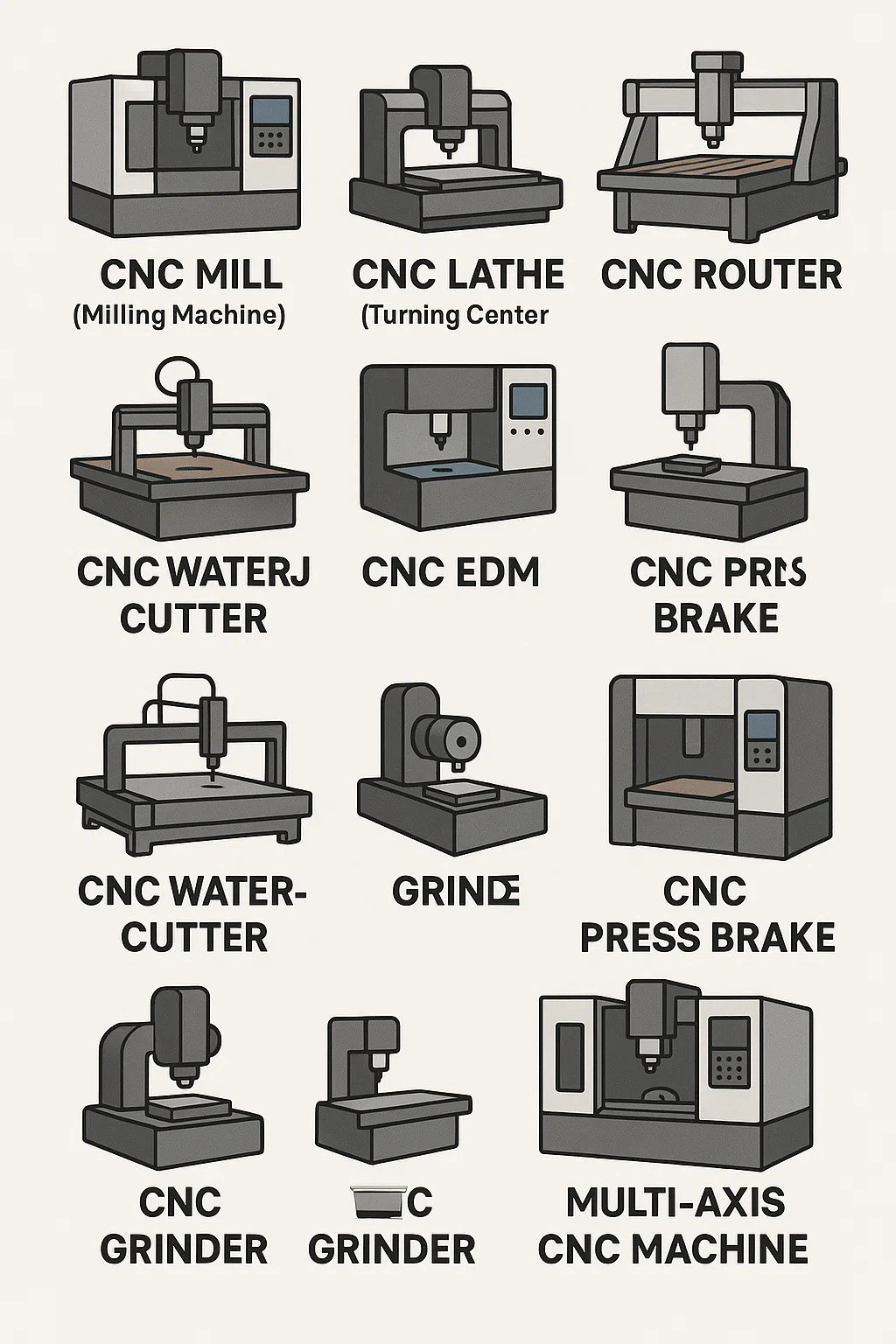
What are CNC machine types?
Here's a breakdown of common CNC machine types you'll find in workshops and factories, explained in plain terms:
●CNC Mills (Milling Machines / Machining Centers):
•What it does: Uses spinning cutting tools to carve away material. Think of a very precise, automated drill that can also move sideways to cut slots, pockets, and complex 3D shapes.
•Key Features: The spindle (holding the tool) usually moves up/down (Z-axis), while the workpiece moves left/right (X-axis) and forward/back (Y-axis). Many have an Automatic Tool Changer (ATC) to swap tools without stopping.
•Common Uses: Making engine parts, molds, brackets, prototypes. Essential for metalworking shops. A CNC machining center is often a more advanced mill with an ATC and enclosure.
●CNC Lathes (Turning Centers):
•What it does: Holds a round workpiece that spins rapidly. Cutting tools then move in to shape the outside diameter, bore the inside, cut grooves, or thread the material.
•Key Features: The workpiece spins in a chuck. Tools move in radially (X-axis) and along the length (Z-axis). Great for making symmetrical, round parts like shafts, bushings, and nozzles. A CNC turning center is a more advanced lathe, often with multiple tools and live tooling (spinning tools for milling/drilling on the part).
●CNC Routers:
•What it does: Similar to a CNC mill but typically designed for softer materials like wood, plastic, foam, and sometimes light metals like aluminum. Often has a larger work area.
•Key Features: Generally less rigid than metal-cutting mills. Common in woodshops, sign-making, furniture building, and prototyping. Can be benchtop CNC models for smaller shops or large industrial machines for cabinetry.
●CNC Plasma Cutters:
•What it does: Uses a super-hot, electrically charged stream of gas (plasma) to melt through metal sheets. A torch moves over the metal following the CNC path.
•Key Features: Primarily for cutting flat sheet metal profiles (like brackets or artwork shapes) quickly. Requires good ventilation. Not for precision machining like milling.
●CNC Laser Cutters:
•What it does: Focuses an intense laser beam to cut or engrave materials. The laser head moves over the material.
•Key Features: Excellent for precise cutting of thin metal sheets, plastics, wood, fabric, and engraving. Creates very clean edges. Power varies greatly depending on material thickness.
●CNC Waterjet Cutters:
•What it does: Uses an extremely high-pressure stream of water, often mixed with an abrasive grit, to erode through material.
•Key Features: Can cut almost any material (metal, stone, glass, composites, rubber) without generating heat (avoids warping or heat-affected zones). Slower than plasma or laser but very versatile for thick or sensitive materials.
●CNC EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining):
•What it does: Uses controlled electrical sparks to erode very hard metal into complex shapes. Doesn't rely on physical cutting force.
Key Types:
•Wire EDM: Uses a thin, electrically charged wire to cut intricate profiles through hardened metal (like making stamping dies).
•Sinker EDM (Ram EDM): Uses a shaped electrode (often copper or graphite) to create cavities or complex shapes in the workpiece.
●CNC Grinders:
•What it does: Uses a spinning abrasive wheel to remove tiny amounts of material, achieving an extremely smooth surface finish and ultra-precise dimensions.
•Common Uses: Finishing hardened metal parts like bearing races, cutting tool edges, or shafts where surface smoothness and exact size are critical.
●CNC Press Brakes:
•What it does: Bends sheet metal along straight lines. A punch presses the metal sheet down into a die to create precise angles and bends.
•Key Features: The CNC controls the position of the back gauge (positions the metal) and the depth/force of the bend. Essential for making metal enclosures, brackets, and chassis parts.
●Multi-Axis CNC Machines:
•What it does: Refers to mills, lathes, or routers that can move in more than the basic 3 directions (X, Y, Z). Common examples:
•4-axis: Adds rotation around the X-axis (A-axis), allowing machining on multiple sides without re-fixturing.
•5-axis: Adds rotation around another axis (like the Y-axis - B-axis, or around the tool - C-axis). Allows incredibly complex shapes to be machined in a single setup (like aerospace parts or turbine blades).
Interested in cooperation or have questions?
-
-
The Core Distinction Between Vertical and Horizontal Machining The fundamental difference between vertical and horizontal machining lies in the orientation of the spindle, which determines how the cutting tool approaches the work...
READ MORE -
Vertical machining is a machining method that uses the vertical movement of a cutting tool to cut materials. If you've ever seen an old-fashioned drill press, or imagine a chef vertically holding a knife and cutting vegetables on ...
READ MORE -
Among the diverse family of CNC machines, vertical machining centers (VMCs) are the most common and versatile. If you walk into a machine shop, you'll likely see more of these machines than any other type. It's like an enhanced,...
READ MORE

-
Factory Address
Zhaxi Township Industrial Park, Nantong City, Jiangsu Province, China (west of Huaneng Power Plant)
-
Phone
+86-13615235768
+86-513-85632335
-
Fax
+86-513-85632766
-
Email
pan.director@sunwayer.com
lf you can't find the answer you're looking for, chat with our friendly team.



 русский
русский Español
Español





