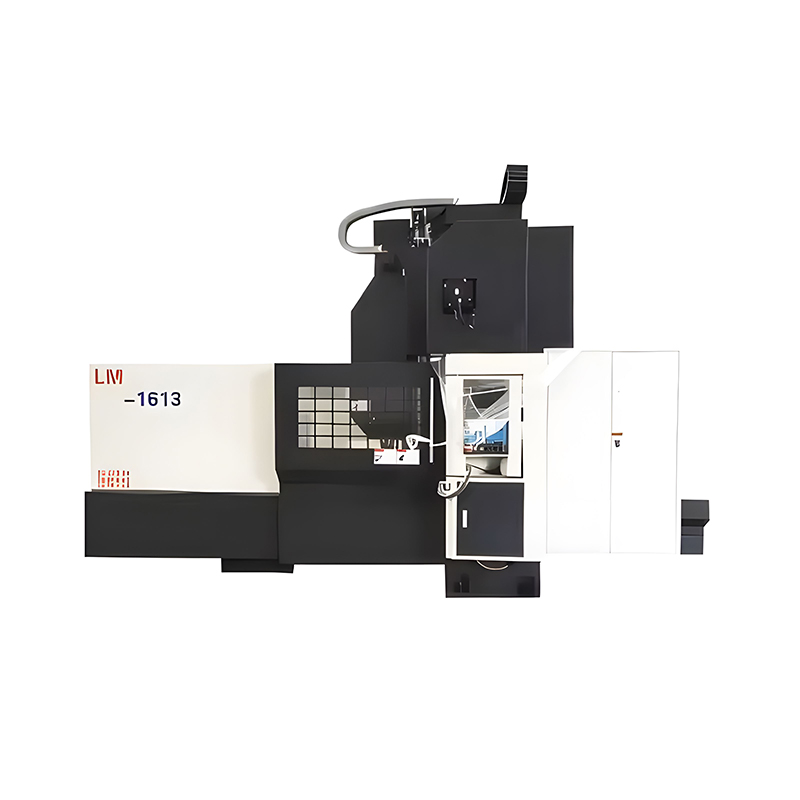
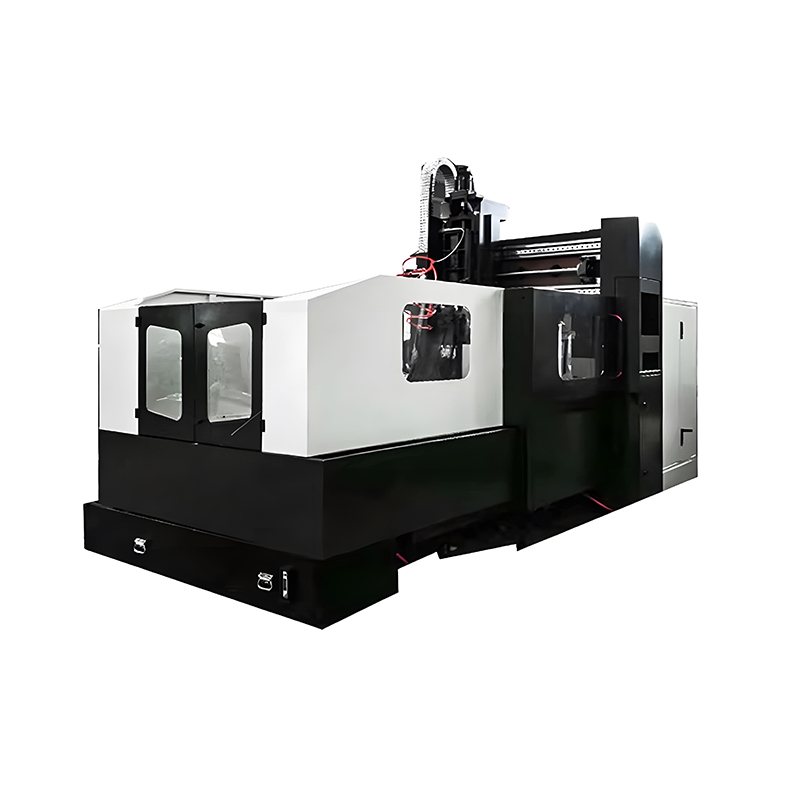
Top Tier Manufacturers of Vertical Machining Centers When searching for the industry leaders in vertical machining centers, several names consistently dominate the market based on reliability, precision, and technological innovat...
READ MOREWe provide quality products and services to customers from all over the world.
Content
- 1 Key Points to Consider Before Buying a CNC Machine
- 1.1 1. Understand Your Machining Needs (What do you plan to use it for?)
- 1.2 2. Number and Type of Axes (How does it move?)
- 1.3 3. Machine Construction and Rigidity (How "strong" is it?)
- 1.4 4. Spindle Selection (The "Motor" of the Cutting Tool)
- 1.5 5. Control System (The "Brain" of the Machine Tool)
- 1.6 6. Maintenance, Consumables, and Operating Costs
What's good to know before buying a CNC machine? (Some buying tips)
Key Points to Consider Before Buying a CNC Machine
Purchasing a CNC machine is a significant investment. Before making a decision, understanding the following points will help you choose the equipment best suited to your needs and ensure its smooth operation.
1. Understand Your Machining Needs (What do you plan to use it for?)
Machining Materials: What types of materials do you primarily intend to machine? For example, if you mainly process wood or soft plastics, the requirements for spindle power and machine rigidity will be lower than for machining steel, titanium, or hard alloys.
Workpiece Size: How large are the parts you typically need to machine? This directly determines the working area (travel) of the CNC machine you need. The table size and the maximum travel distance of the X/Y/Z axes are crucial.
Machining Accuracy and Surface Finish: What are the requirements for dimensional accuracy and surface quality of your products? Higher accuracy requirements usually necessitate more expensive, more robust machines, higher quality guide rails, and more precise drive systems.
Machining Type: Do you primarily perform 2D cutting, 3D engraving, drilling, or milling? For example, complex curved surface machining (3D engraving) may require multi-axis capabilities.
2. Number and Type of Axes (How does it move?)
3-axis machine: This is the most common type, allowing the cutting tool to move in three basic directions (X, Y, Z). It is ideal for planar machining and the manufacturing of many general-purpose parts.
4-axis or 5-axis machine: These add rotational axes (e.g., A-axis or B-axis), allowing machining of the workpiece from more angles, reducing the number of setups, and are necessary for complex parts (such as blades or molds).
Selection Tip: For most entry-level applications and hobbyist projects, a 3-axis CNC machine is sufficient.
3. Machine Construction and Rigidity (How "strong" is it?)
Machine Body Material: The machine frame is usually made of cast iron, steel, or granite composite materials. Cast iron and steel structures are heavier and more stable, better absorbing vibrations generated during cutting. Less vibration results in higher machining accuracy and surface quality.
Guide Rail Type:
Sliding guide rails (hard rails): Strong load-bearing capacity, suitable for heavy cutting, but with higher friction during movement. Linear Guides (Linear Rails): Low friction, high positioning accuracy, and fast movement speed, suitable for high-speed and high-precision machining.
Rigidity Impact: If you plan to perform heavy cutting or machine hard materials, prioritize a heavier, more robust CNC machine to ensure stable cutting.
4. Spindle Selection (The "Motor" of the Cutting Tool)
Power: The spindle's power determines how fast and deep it can cut materials. Machining wood may only require a few hundred watts, while machining hard metals requires several kilowatts or even more.
Rotational Speed (RPM): Different materials and tools require different rotational speeds. Machining wood and soft materials usually requires high speeds (e.g., over 18,000 RPM), while machining metals may require higher torque at lower speeds.
Cooling Method:
Air Cooling: Simple structure, easy maintenance, but noisier.
Water Cooling: Good cooling effect, low noise, but requires additional water circulation system maintenance.
5. Control System (The "Brain" of the Machine Tool)
Ease of Use: The control system is the interface through which you interact with the CNC machine. Some systems are powerful but complex to operate (e.g., Fanuc, Siemens, Heidenhain), while others (e.g., Mach3, GRBL) are more suitable for small machines and hobbyists and are relatively easy to learn.
Programming: Understand whether your control system supports the programming languages or software (CAM software) you commonly use.
Updates and Support: The reliability of the system, the manufacturer's ongoing support for the control system, and software update capabilities are also factors to consider.
6. Maintenance, Consumables, and Operating Costs
Routine Maintenance: All CNC machines require regular lubrication, cleaning, and calibration. Understand the complexity of routine maintenance.
Tools and Fixtures: After purchasing the machine, you will also need to invest in a set of suitable cutting tools and fixtures for holding the workpiece (such as vises, suction cups, or clamping systems).
Power Requirements: Confirm that your facility has sufficient power supply (e.g., single-phase 220V or industrial three-phase 380V) to power the spindle and all motors.
Additional Equipment: Do you need additional chip removal systems, oil mist collectors, or coolant systems? These will increase initial investment and operating costs.

NEXT:What do you make with your CNC machines? (Introduction/Guide)
Interested in cooperation or have questions?
-
-
The Core Distinction Between Vertical and Horizontal Machining The fundamental difference between vertical and horizontal machining lies in the orientation of the spindle, which determines how the cutting tool approaches the work...
READ MORE -
Vertical machining is a machining method that uses the vertical movement of a cutting tool to cut materials. If you've ever seen an old-fashioned drill press, or imagine a chef vertically holding a knife and cutting vegetables on ...
READ MORE -
Among the diverse family of CNC machines, vertical machining centers (VMCs) are the most common and versatile. If you walk into a machine shop, you'll likely see more of these machines than any other type. It's like an enhanced,...
READ MORE

-
Factory Address
Zhaxi Township Industrial Park, Nantong City, Jiangsu Province, China (west of Huaneng Power Plant)
-
Phone
+86-13615235768
+86-513-85632335
-
Fax
+86-513-85632766
-
Email
pan.director@sunwayer.com
lf you can't find the answer you're looking for, chat with our friendly team.



 русский
русский Español
Español





