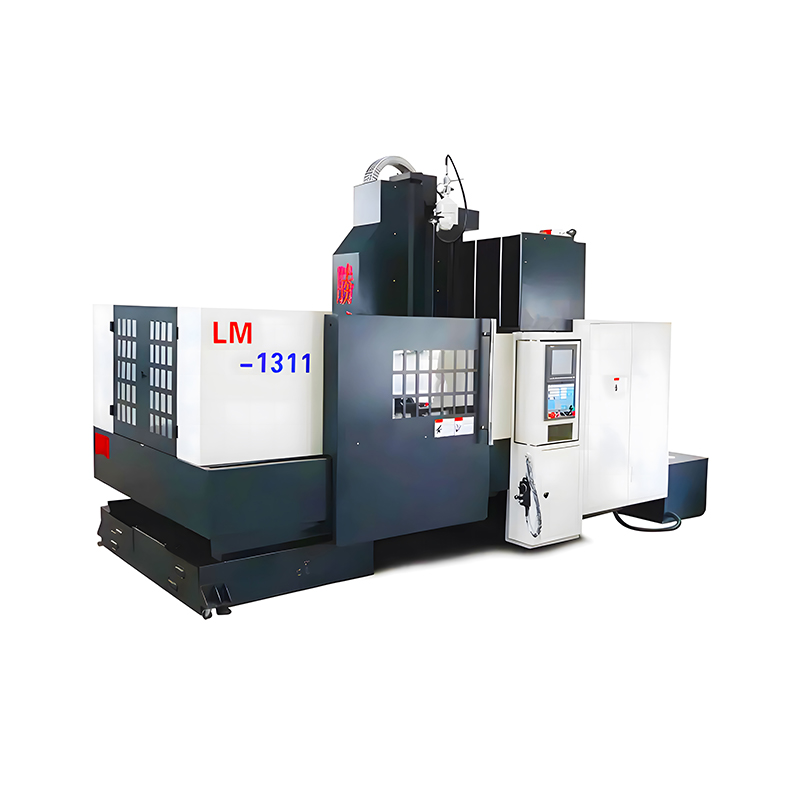
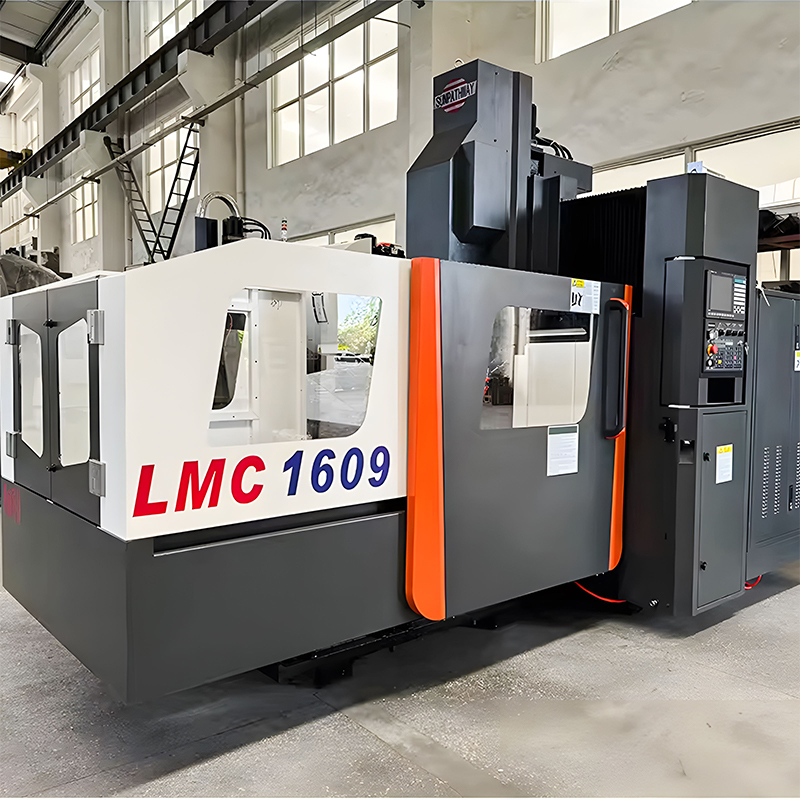
For beginners, the ideal CNC machine isn't necessarily the most powerful one, but rather the one that makes you "confident enough to get started" and has a "high tolerance for errors." Here are a few types of machines suitable for...
READ MOREWe provide quality products and services to customers from all over the world.
Content
- 1 Basic Definition & Scope
- 2 Core Functions & Applications
- 3 Typical Buyer Queries
- 4 Key Specification Checklist
- 5 Buying Options & Decision Factors
- 6 Recommended Pre‑Purchase Actions
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions
- 8 Purchasing Process & Tips
- 9 Material‑Specific Guidance
- 10 Common Maintenance Checklist (Monthly)
- 11 Where to Find Reliable Information
- 12 Frequently Overlooked Factors
- 13 Quick Reference Checklist
- 14 Additional Quick Tips
- 15 Further Concise Points
CNC Engraving Milling Machine – Knowledge Guide
Basic Definition & Scope
What is a CNC engraving milling machine? – a gantry‑type or router‑style CNC that can both mill (remove material) and engrave (shallow, high‑speed cuts) on metal, wood, plastic, acrylic, PCB, etc.
Core Functions & Applications
| Function | Typical Use | Key Benefit |
| High‑speed engraving | Fine text, logos, QR codes on metal, wood, acrylic | Very small‑diameter tools → high spindle speeds needed |
| Precision milling | 3‑D contours, pockets, slots, aerospace parts | Sub‑micron positioning accuracy (≤ 0.01 mm) |
| Multi‑axis machining (3‑5 axis) | Complex geometries, aerospace, medical implants | Reduces setup time, improves surface finish |
| Automatic tool change (ATC) | Continuous production runs | Minimises downtime, supports mixed‑material jobs |
| Sub‑spindle / secondary spindle | Simultaneous milling & engraving, deep‑hole drilling | Increases productivity for heavy‑duty work |
| Integrated coolant & lubrication | Metal cutting, long‑run stability | Extends tool life, improves chip evacuation |
| Safety & environmental features | Dust extraction, enclosure, emergency stop | Meets modern safety standards |
Typical Buyer Queries
| Category | Representative Search Terms |
| Machine specifications | “CNC engraving milling machine spindle speed”, “max feed rate CNC router”, “axis travel CNC engraving” |
| Tooling & accessories | “CNC router bits for engraving”, “ATC tool changer options”, “sub‑spindle kits” |
| Performance & accuracy | “CNC engraving machine repeatability”, “precision tolerance CNC milling” |
| Software & control | “G‑code editor for CNC engraving”, “CAM software compatibility”, “touchscreen CNC controller” |
| Automation & integration | “CNC machine automatic loading unloading”, “robotic pallet changer CNC” |
| Safety & certifications | “CNC engraving machine CE certification”, “ISO safety standards CNC mill” |
| Pricing & financing | “used CNC engraving mill price”, “new CNC router cost 2024”, “CNC machine lease options” |
| After‑sale support | “spare parts CNC milling”, “training for CNC engraving”, “warranty terms CNC machine” |
| Industry suitability | “CNC engraving for metal jewelry”, “wood CNC router for furniture”, “aerospace CNC milling requirements” |
| Environmental & sustainability | “energy‑efficient CNC milling”, “low‑noise CNC engraving” |
Key Specification Checklist
▸Spindle Speed – Minimum 12 000 rpm for fine engraving; 24 000 rpm+ for micro‑detail work.
▸Power & Torque – 2.2 kW (3 HP) minimum for metal; 5 kW+ for heavy‑duty alloys.
▸Travel (X‑Y‑Z) – Typical ranges: 600 × 400 × 300 mm (small), up to 2000 × 1200 × 800 mm (large).
▸Accuracy & Repeatability – ±0.01 mm (high‑precision) or better.
▸Tool Capacity – ATC magazine 20–30 tools; optional sub‑spindle.
▸Control System – Fanuc, Siemens, or proprietary touchscreen with Ethernet/USB.
▸Cooling – Flood coolant, mist, or dry‑air system; check filtration.
▸Safety – Enclosed work area, emergency stop, interlocks, noise ≤ 80 dB.
▸Software Compatibility – Fusion 360, Mastercam, SolidWorks CAM, or proprietary CAM.
▸Power Requirements – 380 V/3‑phase typical; verify local voltage.
Buying Options & Decision Factors
| Option | Advantages | Considerations |
| New machine | Full warranty, latest tech, manufacturer support | Higher upfront cost |
| Used machine | Lower price, proven reliability, quick availability | Verify wear on spindle, controller version, availability of spare parts |
| OEM custom build | Tailored axis travel, spindle, automation | Longer lead time (25‑30 days typical) |
| Leasing / Financing | Cash‑flow friendly, upgrade path | Total cost may exceed outright purchase |
| Bundle with tooling | One‑stop solution (bits, coolant, software) | Ensure tool quality matches material needs |
Recommended Pre‑Purchase Actions
▸Define Application – Material (metal, wood, acrylic), part size, production volume.
▸Create a Spec Sheet – List required spindle speed, travel, accuracy, tool capacity.
▸Request Quotations – From at least three suppliers; ask for CAD‑compatible machine data.
▸Check Certifications – CE, ISO 9001, local safety standards.
▸Ask for Demo / Trial Run – On a sample part to verify surface finish and cycle time.
▸Evaluate After‑Sale Service – Spare‑part lead time, on‑site training, remote support.
▸Review Total Cost of Ownership – Energy consumption, tooling wear, maintenance contracts.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.Can a CNC milling machine be used for engraving?
Yes; any CNC mill can perform engraving, but high‑speed spindles improve quality.
2.What is the typical warranty period?
12 months for standard machines; 24 months optional for premium models.
3.Do I need a separate CAM software for engraving?
Most machines accept standard G‑code; dedicated CAM (e.g., Vectric Aspire) simplifies toolpath creation.
4.How important is the coolant system for engraving metal?
Critical for tool life and surface finish; flood coolant is recommended for steel/aluminum.
5.Is an automatic tool changer necessary?
For production runs > 100 parts, ATC reduces cycle time dramatically.
Purchasing Process & Tips
▸Verify specifications against actual needs – material, part size, production volume.
▸Compare multiple suppliers – price, warranty, after‑sales support, spare‑part availability.
▸Consider used or refurbished units for entry‑level budgets, but inspect wear on spindle bearings and linear guides.
▸Check for certifications & safety compliance – CE, ISO, local electrical standards.
▸Plan for software & training – ensure the vendor provides CAD/CAM packages or compatible third‑party licenses, plus operator training.
Material‑Specific Guidance
| Material | Recommended Spindle Speed | Tool Type | Coolant / Lubrication |
| Aluminum | 12 000–18 000 rpm | Carbide 1‑mm engraving bit | Mist or flood coolant |
| Stainless steel | 8 000–12 000 rpm | Cobalt or TiAlN coated carbide | Flood coolant, high pressure |
| Brass / Copper | 12 000–20 000 rpm | Sharp carbide or diamond tip | Light mist |
| Wood (hard) | 18 000–24 000 rpm | High‑speed steel (HSS) or carbide | Dry or light mist |
| Acrylic / Plastics | 15 000–24 000 rpm | Single‑flute carbide | Dry (to avoid melting) |
Common Maintenance Checklist (Monthly)
▸Spindle oil level & filter – Replace oil every 200 h.
▸Linear guide lubrication – Apply grease to rails.
▸Tool holder inspection – Check for wear, replace collets if needed.
▸Coolant filtration – Clean or replace filter cartridges.
▸Electrical connections – Tighten terminal blocks, inspect wiring.
▸Software backup – Export machine parameters and NC programs.
Where to Find Reliable Information
▸Manufacturer datasheets (PDF) – primary source for specs.
▸Industry forums (Practical Machinist, CNCZone) – user experiences, reliability data.
▸Trade shows (EMO Hannover, China CNC Expo) – live demos, latest tech.
▸Third‑party reviews (YouTube channels: NYC CNC, This Old Tony) – performance benchmarks.
Frequently Overlooked Factors
▸Power quality – install UPS or voltage stabilizer for spindle protection.
▸Floor load – verify machine weight vs. shop floor capacity (often > 2 t).
▸Noise compliance – ensure ≤ 85 dB for indoor use.
Quick Reference Checklist
| Item | Details |
| Spindle speed ≥ 12 k rpm | Engraving fine detail |
| ATC capacity ≥ 20 tools | Production efficiency |
| Accuracy ≤ 0.01 mm | High‑precision parts |
| Coolant system | Flood or mist, filtration |
| Safety enclosure & E‑stop | Regulatory compliance |
| Warranty ≥ 12 months | After‑sale support |
| Power requirement | Match local supply (380 V/3‑φ) |
| Software compatibility | G‑code + CAM (Fusion, Mastercam) |
| Total Cost of Ownership | Include energy, consumables |
Additional Quick Tips
▸Tool selection: For metal engraving use 0.5‑1 mm carbide bits; for wood choose 2‑3 mm high‑speed steel bits.
▸Calibration: Run a 3‑point probe routine weekly to maintain ≤ 0.01 mm repeatability.
▸Software workflow: CAD → CAM (toolpath) → post‑processor → CNC (G‑code). Verify preview before machining.
▸Upgrade path: Choose a machine with modular ATC and optional sub‑spindle to avoid future replacement.
▸Vendor vetting: Ask for at least three recent customer references and a copy of the service SLA.
Further Concise Points
▸Dust extraction: Install a HEPA‑rated extractor when machining wood or composites.
▸Energy use: 5‑axis machines typically draw 5–7 kW; consider an energy‑monitoring plug to track costs.
▸Remote monitoring: Choose a controller with Ethernet/IoT dashboard for real‑time status and alerts.
▸Spindle maintenance: Replace bearings after ~2 000 h of high‑speed operation to prevent run‑out.
▸Software licensing: Opt for perpetual CAM licenses if long‑term cost is a concern; otherwise, annual subscriptions may include updates.
▸Training resources: Manufacturer‑provided webinars, plus free online courses (e.g., CNC Academy) accelerate operator proficiency.
▸Resale value: Machines with documented maintenance logs retain > 70 % of original price after 5 years.
| Category | Typical Search Queries (English) | Key Information Buyers Expect |
| 1. Machine Types & Configurations | “vertical vs. horizontal CNC engraving mill”, “5‑axis CNC engraving machine”, “mini CNC router for engraving” | Differences in spindle orientation, axis count, work‑area size, modular accessories, suitability for 2‑D vs. 3‑D engraving. |
| 2. Core Specifications | “CNC engraving mill spindle power”, “bed size CNC router engraving”, “spindle speed range for metal engraving”, “tool holder size CNC mill” | Spindle power (kW or HP), max RPM, travel dimensions (X × Y × Z), tool changer capacity, controller type, repeatability/precision (µm). |
| 3. Material Compatibility | “what materials can CNC engraving mill cut”, “engraving acrylic vs. aluminum CNC”, “best cutter for wood engraving” | List of compatible substrates (wood, MDF, acrylic, ABS, polycarbonate, aluminum, brass, PCB, foam, wax), recommended cutter types (V‑bit, ball‑nose, T‑bit, carbide end‑mill). |
| 4. Software & Control | “CNC engraving software G‑code”, “best CAM for CNC milling”, “GRBL vs. Mach3 for engraving” | CAM packages (Fusion 360, SolidWorks CAM, LightBurn, Candle), controller firmware (GRBL, LinuxCNC, proprietary), file formats (DXF, STL, SVG), simulation & preview features. |
| 5. Performance & Accuracy | “CNC engraving mill tolerance”, “repeatability of 5‑axis engraver”, “how to measure spindle run‑out” | Typical positioning accuracy (±0.01 mm), repeatability, backlash compensation, spindle run‑out specs, impact on fine detail engraving. |
| 6. Cost & ROI | “price of CNC engraving mill 2024”, “budget CNC router for small business”, “total cost of ownership CNC milling” | Price ranges (entry‑level 2k–5k, mid‑range 10k–30k, high‑end >$50k), optional accessories (vacuum table, coolant system), maintenance costs, expected lifespan, productivity gains. |
| 7. After‑Sales Support & Training | “CNC engraving machine warranty”, “technical support for CNC mill”, “training videos for CNC router” | Warranty period, on‑site service, spare‑part availability, training resources (manuals, video tutorials, one‑on‑one technician help). |
| 8. Safety & Compliance | “CNC milling machine safety features”, “ISO certification CNC router”, “dust extraction for engraving mill” | Enclosed safety cages, emergency stop, limit switches, dust extraction/filtration, CE/ISO certifications. |
| 9. Integration & Automation | “CNC mill with automatic tool changer”, “IoT enabled CNC engraving”, “robotic loading for CNC router” | ATC (automatic tool changer) capacity, PLC integration, remote monitoring, data logging, compatibility with Industry 4.0 platforms. |
| 10. Application Examples | “CNC engraving for PCB prototyping”, “custom signage CNC milling”, “metal jewelry engraving machine” | Typical use‑cases: PCB drilling/engraving, signage & nameplates, decorative wood/foam parts, metal jewelry, small‑batch production of mechanical components. |
| Category | Sample searches | What buyers look for |
| 11. Upgrades & Accessories | “CNC mill coolant system retrofit”, “laser engraving add‑on for CNC router” | Compatibility of water/air coolant, laser modules, rotary axis, probe kits. |
| 12. Precision Enhancements | “linear rails vs. ball screws CNC”, “servo vs. stepper motor for engraving” | Benefits of linear guideways, servo drives for higher speed/accuracy, maintenance differences. |
| 13. Noise & Vibration | “quiet CNC engraving machine”, “vibration isolation for CNC router” | Enclosed cabinets, dampening pads, spindle mounting options. |
| 14. Shipping & Installation | “CNC milling machine delivery China”, “factory setup service CNC router” | Packaging dimensions, freight cost, on‑site assembly, calibration service. |
| 15. Reviews & Comparisons | “best CNC engraving mill 2024 review”, “XYZ vs. Haas CNC router comparison” | User ratings, reliability statistics, after‑sales support feedback. |
| Category | Typical queries | Key points buyers need |
| 16. Power & Electrical | “CNC router voltage requirement”, “phase‑3 power for 10 kW spindle” | Input voltage (220 V/380 V), three‑phase vs. single‑phase, power consumption, UPS compatibility. |
| 17. Software Licensing | “Fusion 360 free for hobby CNC”, “Mach3 perpetual license cost” | Free tiers, subscription models, number of axes supported, update policy. |
| 18. Maintenance & Spare Parts | “CNC spindle bearing replacement”, “linear guide wear signs” | Recommended service intervals, part numbers, availability of OEM vs. third‑party components. |
| 19. Environmental Limits | “CNC router operating temperature range”, “humidity effect on CNC accuracy” | Operating temp (5‑40 °C), humidity control, dust‑proof rating (IP). |
| 20. Financing & Leasing | “CNC milling machine lease options”, “equipment loan for CNC router” | Lease terms, interest rates, tax benefits, buy‑out options. |
NEXT:CNC Gantry Milling Machine Comprehensive Knowledge Guide
Interested in cooperation or have questions?
-
-
Operating a CNC machine is like flying a plane or performing surgery; although the movements become smooth with practice, even the slightest oversight can lead to costly losses. A checklist isn't meant to restrict your freedom, bu...
READ MORE -
Although many people recommend starting with simpler equipment, choosing a 5-axis CNC machine from the outset is actually a smart "one-step" strategy. For those who want to develop a long-term career in manufacturing, the advantag...
READ MORE -
Key Points to Consider Before Buying a CNC Machine Purchasing a CNC machine is a significant investment. Before making a decision, understanding the following points will help you choose the equipment best suited to your needs and...
READ MORE

-
Factory Address
Zhaxi Township Industrial Park, Nantong City, Jiangsu Province, China (west of Huaneng Power Plant)
-
Phone
+86-13615235768
+86-513-85632335
-
Fax
+86-513-85632766
-
Email
pan.director@sunwayer.com
lf you can't find the answer you're looking for, chat with our friendly team.



 русский
русский Español
Español





